Pashmina is the worlds’ most sought after natural fiber produced by Pashmina goat - a double-coated animal with an outer coat of long coarse guard hair and inner coat of shorter fine down fiber pashmina/cashmere. Pashmina fiber present an excellent model for studying hair biology due to annual cycle that exhibits seasonal rhythms with a well-defined and synchronized duration of fiber growth. Here, we present an expression database of significantly dysregulated genes between different fiber cycling stages viz active growth (anagen), fiber resting phase (telogen) and fiber regression phase (catagen). This web portal offers an informative and flexible ways to display gene expression profiles by specifying a gene name (e.g., (AKT2, SNRPE, FGF10, etc ),and its expression profiles (in FPKM) across different fiber developmental stages were displayed using heatmaps along-with the gene annotation. To facilitate visualization of expression profiles, enriched GO terms and pathways interactive heatmaps, scatter-plots, and chord-graphs are used. This is the first effort for enhancing data visibility and understanding essential biological mechanisms underlying complex agronomic traits in pashmina goat.
PHP v5.6 and Perl v5.6 are used for server-side programming, MySQL v5.7 for data storage and AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) for data retrieving from the database. The database has been thoroughly tested on the commonly available web-browsers like Google chrome, Safari, Mozilla Firefox and Internet explorer. It supports text query where user can input gene name in the search box. The search results present the information on level of gene expression in different fiber developmental stages, their function, pathway(s) involved in, protein class, GO terms and protein-protein interaction network.
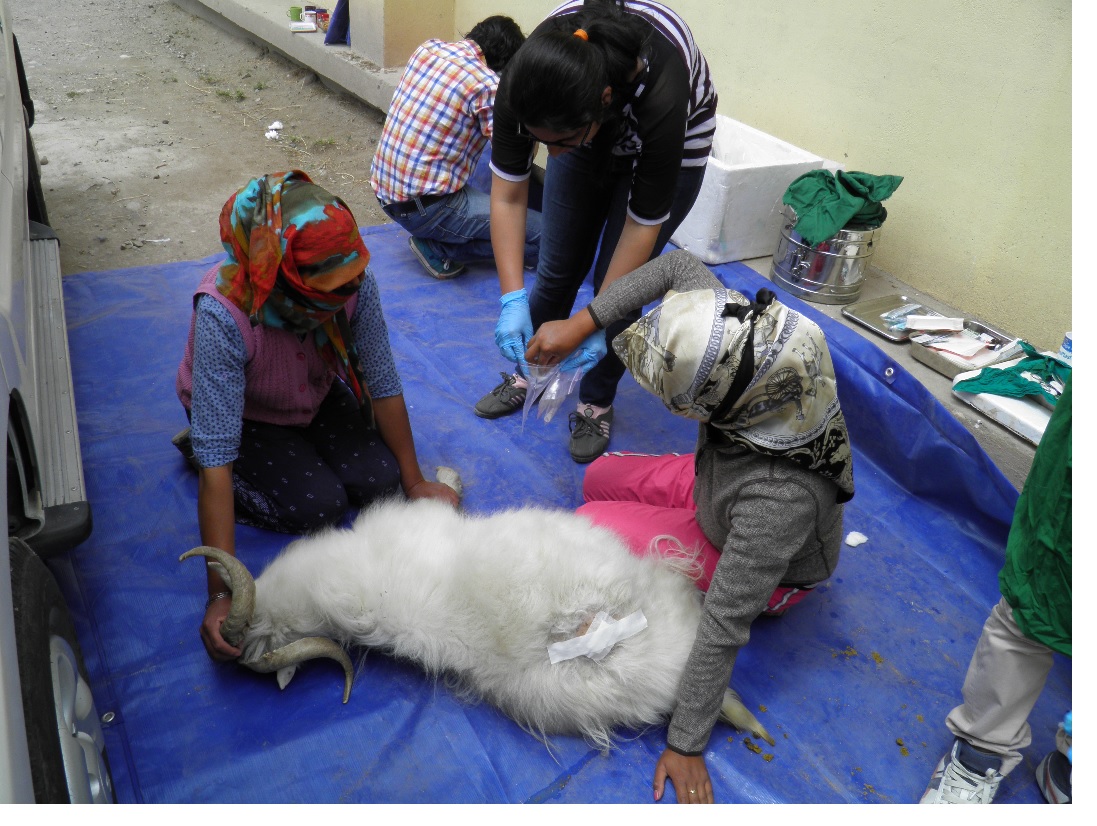
Three unrelated pashmina goats of the same age (26 months) and sex (doves) were taken at four stages (Catagen-C, Telogen-T, early Anagen-eA and late Anagen-lA) revealed a total of 2116 DEGs for four sequential transition phases (CT, TA, eA/lA and AC).